
大昌華嘉科學儀器部
 白金會員
白金會員 已認證
已認證

大昌華嘉科學儀器部
 白金會員
白金會員 已認證
已認證
New High-Throughput Method for Elastin-like Polymer (ELP) Coacervate Analysis
彈性蛋白聚合物(ELP)凝聚層分析的新型高通量方法
Posted by Michelle Devoe
Michelle Devoe發表
December 2018 — A recent study by researchers from the University of New England and University of New Hampshire has demonstrated that flow imaging microscopy is an accurate, more efficient, and more informative method of elastin-like polymer (ELP) coacervate analysis than standard methods. ELP coacervates are a class of molecules with promising applications in drug delivery vehicles, tissue engineering, environmental remediation, and more. ELP coacervate architecture is stimuli-responsive and highly tunable, making them ideal for the above-mentioned applications.
2018年12月 - 新英格蘭大學和新罕布什爾大學的研究人員最近的一項研究表明,與標準方法相比,流動成像顯微鏡是一種準確,更有效,信息更豐富的彈性蛋白樣聚合物(ELP)凝聚分析方法。 ELP凝聚層在作為藥物遞送的載體,組織工程,環境修復等方面具有廣闊的應用前景。 ELP凝聚層結構具有刺激響應性和高度可調性,使其成為上述應用的理想選擇。
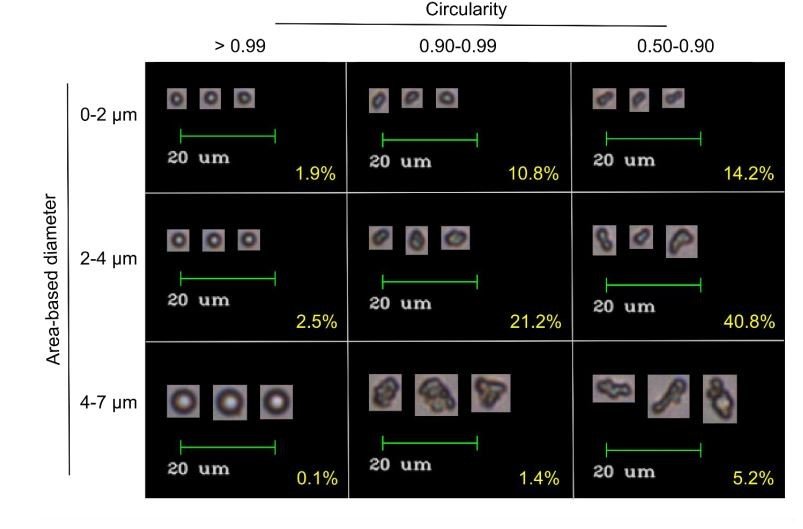
ELP coacervates imaged by the FlowCam. Size and circularity, two of the 40+ properties that can be measured by the FlowCam, is used to sort coacervates. Image from Marvin et al. (2018).
ELP凝聚了由FlowCam成像的圖像。 尺寸和圓度是FlowCam可以測量的40多個屬性中的兩個,用于對凝聚層進行分類。 圖片來自Marvin等。(2018)。
Standard methods for ELP coacervate analysis are indirect and cumbersome. Data from Visible-UV spectrophotometer turbidity measurements and dynamic light scattering (DLS) size measurements are superimposed to evaluate the formation of micron-scale aggregates, and particle geometry is constructed indirectly from diffusion data. Imaging analysis methods such as optical, electron, and scanning probe microscopy are useful methods to acquire size and shape data, however it is time-consuming and laborious to acquire a large enough sample size to get statistically significant data.
ELP凝聚層分析的標準方法是間接和麻煩的。 來自可見 - 紫外分光光度計濁度測量和動態光散射(DLS)尺寸測量的數據被疊加以評估微米級聚集體的形成,并且顆粒幾何形狀間接地由擴散數據構建。 諸如光學,電子和掃描探針顯微鏡之類的成像分析方法是獲取尺寸和形狀數據的有用方法,然而獲得足夠大的樣本大小以獲得統計上有效的數據是耗時且費力的。
In this study by the University of New England and University of New Hampshire, the size, morphology, and behavior of ELP coacervates subjected to various solvent conditions were measured and observed using the FlowCam particle analyzer. Results were validated by comparison with DLS and atomic force microscopy analyses. Flow imaging microscopy was demonstrated to be a successful method for ELP coacervate analysis. Additionally, flow imaging microscopy reported additional findings that were not measured using the DLS, microscopy, or Visible-UV spectrophotometry.
在新英格蘭大學和新罕布什爾大學的這項研究中,使用FlowCam顆粒分析儀測量和觀察經受各種溶劑條件的ELP凝聚層的尺寸,形態和行為。 通過與DLS和原子力顯微鏡分析的比較驗證結果。 流動成像顯微鏡被證明是ELP凝聚層分析的成功方法。 此外,流動成像顯微鏡提供了DLS,顯微鏡或可見紫外分光光度法不能獲得的結果。
相關產品
更多
相關文章
更多
技術文章
2024-10-09技術文章
2024-08-10技術文章
2024-05-30技術文章
2024-05-30
虛擬號將在 秒后失效
使用微信掃碼撥號